2023
dlg
Sarvestani, A., Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
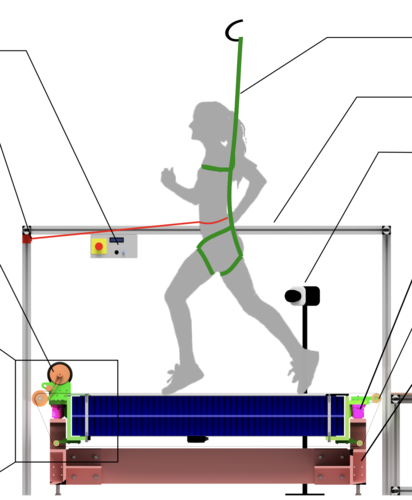
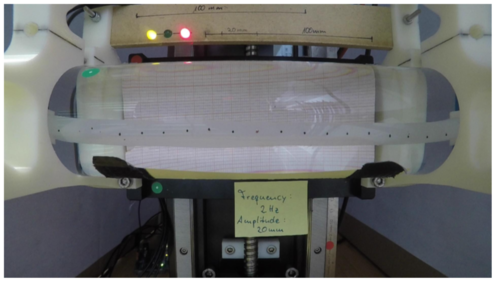
An Open-Source Modular Treadmill for Dynamic Force Measurement with Load Dependant Range Adjustment
2023 (unpublished) Submitted
ei
Berenz, V., Widmaier, F., Guist, S., Schölkopf, B., Büchler, D.
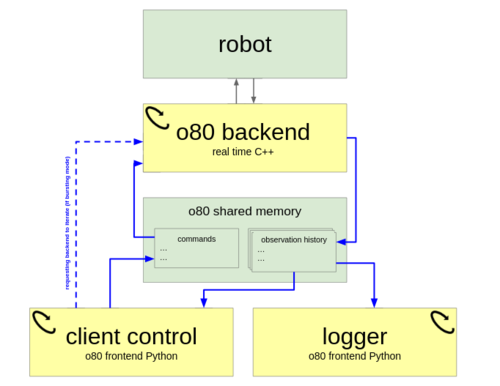
Synchronizing Machine Learning Algorithms, Realtime Robotic Control and Simulated Environment with o80
Robot Software Architectures Workshop (RSA) 2023, ICRA, 2023 (techreport)
ev
Elich, C., Kirchdorfer, L., Köhler, J. M., Schott, L.
Challenging Common Assumptions in Multi-task Learning
abs/2311.04698, CoRR/arxiv, 2023 (techreport)
2022
dlg
Ruppert, F., Badri-Spröwitz, A.
Learning Plastic Matching of Robot Dynamics in Closed-Loop Central Pattern Generators: Data
Edmond, May 2022 (techreport)
ei
Schölkopf, B., Uhler, C., Zhang, K.
Proceedings of the First Conference on Causal Learning and Reasoning (CLeaR 2022)
177, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, PMLR, April 2022 (proceedings)
dlg
pi
Badri-Spröwitz, A., Sarvestani, A. A., Sitti, M., Daley, M. A.
Data for BirdBot Achieves Energy-Efficient Gait with Minimal Control Using Avian-Inspired Leg Clutching
Edmond, March 2022 (techreport)
ev
Li, H., Stueckler, J.
Observability Analysis of Visual-Inertial Odometry with Online Calibration of Velocity-Control Based Kinematic Motion Models
abs/2204.06651, CoRR/arxiv, 2022 (techreport)
2021
ei
Field, A., Prabhumoye, S., Sap, M., Jin, Z., Zhao, J., Brockett, C.
Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on NLP for Positive Impact
Association for Computational Linguistics, August 2021 (proceedings)
re
Lieder, F., Prentice, M., Corwin-Renner, E.
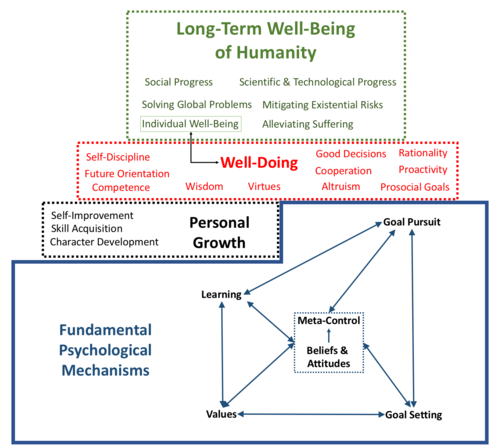
Toward a Science of Effective Well-Doing
May 2021 (techreport)
re
Consul, S., Stojcheski, J., Felso, V., Lieder, F.
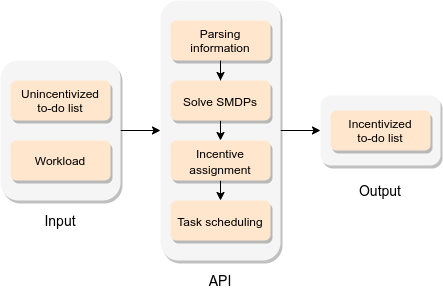
Optimal To-Do List Gamification for Long Term Planning
arXiv preprint arXiv:2109.06505, 2021 (techreport)
2020
re
Stojcheski, J., Felso, V., Lieder, F.
Optimal To-Do List Gamification
ArXiv Preprint, 2020 (techreport)
icm
Dertli, Denis
Nichtgleichgewichtsdynamik einer abgekühlten kritischen Flüssigkeit mit Oberflächenfeldern unterschiedlichen Vorzeichens
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, January 2020 (thesis)
ev
25th International Symposium on Vision, Modeling and Visualization, VMV 2020
(Editors: Jens Krüger and Matthias Nießner and Jörg Stückler), Eurographics Association, 2020 (proceedings)
am
ics
Marco, A., Rohr, A. V., Baumann, D., Hernández-Lobato, J. M., Trimpe, S.
Excursion Search for Constrained Bayesian Optimization under a Limited Budget of Failures
2020 (proceedings) In revision
ics
Baumann, D., Solowjow, F., Johansson, K. H., Trimpe, S.
Identifying Causal Structure in Dynamical Systems
2020 (techreport)
2019
ei
Lutz, P.
Automatic Segmentation and Labelling for Robot Table Tennis Time Series
Technical University Darmstadt, Germany, August 2019 (thesis)
icm
Pranjić, Daniel
Fluctuating interface with a pinning potential
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
lds
Muehlebach, M.
The Silver Ratio and its Relation to Controllability
2019 (techreport)
icm
Beyer, David Bernhard
Controlling pattern formation in the confined Schnakenberg model
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
pf
Itzigehl, Selina
HPLC separation of ligand-exchanged gold clusters with atomic precision
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2019 (thesis)
2018
ev
Ma, L., Stueckler, J., Wu, T., Cremers, D.
Detailed Dense Inference with Convolutional Neural Networks via Discrete Wavelet Transform
arxiv, 2018, arXiv:1808.01834 (techreport)
dlg
Richter, J.
Untersuchung und Charakterisierung von Teilelementen der Modifikation im Lumbosacralbereich von Vögeln
Hochschule Harz, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Maihöfer, Michael
Pattern forming systems under confinement
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Bebon, Rick
Electrostatic interaction between colloids with constant surface potentials at fluid interfaces
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Wilke, Moritz
Non-equilibrium dynamics of a binary solvent around heated colloidal particles
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
lds
Muehlebach, M., D’Andrea, R.
On the Approximation of Constrained Linear Quadratic Regulator Problems and their Application to Model Predictive Control
2018 (techreport)
slt
Keriven, N., Garreau, D., Poli, I.
NEWMA: a new method for scalable model-free online change-point detection
2018 (techreport)
icm
Meiler, Tim
Monte Carlo study of colloidal structure formation at fluid interfaces
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
pf
Hornberger, Lea-Sophie
DNA-linked gold nanoclusters
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
icm
Sattler, Alexander
Surface structure of liquid crystals
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
pf
Vogt, Pascal
HPLC-Trennung von Gold-clustern
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2018 (thesis)
2017
icm
Hölzl, Christian
Non-equilibrium forces after temperature quenches in ideal fluids with conserved density
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
pf
Troll, Jonas
Enzyme activity and transport in biological media
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
pf
Segreto, Nico
Propulsion of magnetic colloids at low Reynolds number
Univ. of Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
zwe-sw
Bramlage, L.
Design of a visualization scheme for functional connectivity data of Human Brain
Hochschule Osnabrück - University of Applied Sciences, 2017 (thesis)
icm
Schmetzer, Timo
Electrostatic interaction between non-identical charged particles at an electrolyte interface
Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, 2017 (thesis)
2016
ei
Ihler, A. T., Janzing, D.
Proceedings of the 32nd Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence (UAI)
pages: 869 pages, AUAI Press, June 2016 (proceedings)
am
ics
Ebner, S., Trimpe, S.
Supplemental material for ’Communication Rate Analysis for Event-based State Estimation’
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, January 2016 (techreport)
2015
am
ics
Trimpe, S.
Distributed Event-based State Estimation
Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, November 2015 (techreport)
ps
Gall, J., Gehler, P., Leibe, B.
Proceedings of the 37th German Conference on Pattern Recognition
Springer, German Conference on Pattern Recognition, October 2015 (proceedings)
ei
Abbott, T., Abdalla, F. B., Allam, S., Amara, A., Annis, J., Armstrong, R., Bacon, D., Banerji, M., Bauer, A. H., Baxter, E., others,
Cosmology from Cosmic Shear with DES Science Verification Data
arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.05552, 2015 (techreport)
ei
Jarvis, M., Sheldon, E., Zuntz, J., Kacprzak, T., Bridle, S. L., Amara, A., Armstrong, R., Becker, M. R., Bernstein, G. M., Bonnett, C., others,
The DES Science Verification Weak Lensing Shear Catalogs
arXiv preprint arXiv:1507.05603, 2015 (techreport)
2014
ps
Freifeld, O., Hauberg, S., Black, M. J.
Model transport: towards scalable transfer learning on manifolds - supplemental material
(9), April 2014 (techreport)
ps
Ahmad, A., Amigoni, A., Awaad, I., Berghofer, J., Bischoff, R., Bonarini, A., Dwiputra, R., Fontana, G., Hegger, F., Hochgeschwender, N., Iocchi, L., Kraetzschmar, G., Lima, P., Matteucci, M., Nardi, D., Schiaffonati, V., Schneider, S.
RoCKIn@Work in a Nutshell
(FP7-ICT-601012 Revision 1.2), RoCKIn - Robot Competitions Kick Innovation in Cognitive Systems and Robotics, March 2014 (techreport)
ps
Ahmad, A., Amigoni, F., Awaad, I., Berghofer, J., Bischoff, R., Bonarini, A., Dwiputra, R., Fontana, G., Hegger, F., Hochgeschwender, N., Iocchi, L., Kraetzschmar, G., Lima, P., Matteucci, M., Nardi, D., Schneider, S.
RoCKIn@Home in a Nutshell
(FP7-ICT-601012 Revision 0.8), RoCKIn - Robot Competitions Kick Innovation in Cognitive Systems and Robotics, March 2014 (techreport)
ps
Tang, S., Andriluka, M., Milan, A., Schindler, K., Roth, S., Schiele, B.
Learning People Detectors for Tracking in Crowded Scenes.
2014, Scene Understanding Workshop (SUNw, CVPR workshop) (unpublished)
2013
ps
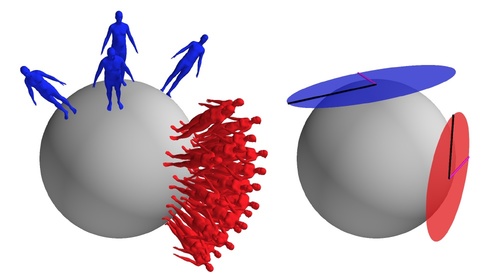
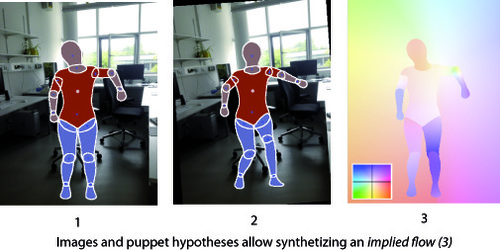
Zuffi, S., Black, M. J.
Puppet Flow
(7), Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, October 2013 (techreport)
ps
Ahmad, A., Awaad, I., Amigoni, F., Berghofer, J., Bischoff, R., Bonarini, A., Dwiputra, R., Hegger, F., Hochgeschwender, N., Iocchi, L., Kraetzschmar, G., Lima, P., Matteucci, M., Nardi, D., Schneider, S.
D2.1.4 RoCKIn@Work - Innovation in Mobile Industrial Manipulation Competition Design, Rule Book, and Scenario Construction
(FP7-ICT-601012 Revision 0.7), RoCKIn - Robot Competitions Kick Innovation in Cognitive Systems and Robotics, sep 2013 (techreport)
ps
Ahmad, A., Awaad, I., Amigoni, F., Berghofer, J., Bischoff, R., Bonarini, A., Dwiputra, R., Hegger, F., Hochgeschwender, N., Iocchi, L., Kraetzschmar, G., Lima, P., Matteucci, M., Nardi, D., Schneider, S.
D2.1.1 RoCKIn@Home - A Competition for Domestic Service Robots
Competition Design, Rule Book, and Scenario Construction
(FP7-ICT-601012 Revision 0.7), RoCKIn - Robot Competitions Kick Innovation in Cognitive Systems and Robotics, sep 2013 (techreport)
ps
Ahmad, A., Awaad, I., Amigoni, F., Berghofer, J., Bischoff, R., Bonarini, A., Dwiputra, R., Fontana, G., Hegger, F., Hochgeschwender, N., Iocchi, L., Kraetzschmar, G., Lima, P., Matteucci, M., Nardi, D., Schiaffonati, V., Schneider, S.
D1.1 Specification of General Features of Scenarios and Robots for Benchmarking Through Competitions
(FP7-ICT-601012 Revision 1.0), RoCKIn - Robot Competitions Kick Innovation in Cognitive Systems and Robotics, July 2013 (techreport)